- Mexican Peso notches minor gains with USD/MXN trading at 17.23, up 0.03%, as investors assess economic indicators from Mexico.
- Mexican GDP growth falls short of expectations, influenced by Banxico’s aggressive interest rate policy now at 11.25%.
- In the US, Consumer Confidence improves and the robust labor market is highlighted by the latest JOLTs report, which could affect Federal Reserve policy.
The Mexican Peso holds minuscule gains versus the US Dollar in early trading during the North American session, sponsored by economic data from Mexico. In the US, the release of the JOLTs reports and Conference Board (CB) Consumer Confidence data could underpin the Greenback (USD), ahead of the US Federal Reserve (Fed) monetary policy decision on Wednesday. The USD/MXN exchanges hands at 17.16, down 0.37%.
Mexico’s economy grew below estimates, revealed the National Statistics Agency (INEGI). Higher interest rates set by the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) at 11.25% is having the desired effect on the economy as the latest GDP data trends lower alongside business activity. Across the border, CB Consumer Confidence improved in January, while the labor market remains hot, according to the JOLTs data.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Mexican Peso barely blinks after GDP figures, awaiting Fed decision
- INEGI revealed that Mexican GDP for Q4 2023 expanded 0.1% QoQ, below forecasts of 0.4% and trailing the 1.1% expansion achieved in the third quarter. For annually based figures, GDP saw its preliminary reading rise by 2.4%, missing forecasts of 3.1% and down from 3.3% in Q3.
- US Job Openings rebounded above the 9 million threshold, the highest level in three months and exceeding estimates of 8.75 million. The data emphasizes the strength of the labor market and might deter Fed officials from cutting rates sooner than expected.
- Further, US data revealed that Consumer Confidence exceeded estimates of 114, coming at 114.8, up from December’s 108. “January’s increase in consumer confidence likely reflected slower inflation, anticipation of lower interest rates ahead, and generally favorable employment conditions as companies continue to hoard labor,” said Dana Peterson, Chief Economist at The Conference Board.
- Today’s data shows the Mexican economy remains strong. Coupled with inflation remaining above Banxico’s target, this could delay the first rate cut by Banxico, even though some officials commented that rate trimming could happen in the first quarter of 2024.
- If Banxico’s officials remain determined to begin its easing cycle in Q1 of 2024, that could depreciate the emerging market currency due to the reduction of interest rate differentials. That could also underpin the USD/MXN pair toward the psychological 18.00 figure.
- Additional factors that might depreciate the Mexican currency are geopolitical risks and risk aversion
- Across the border, the US economy remains resilient, as GDP in Q4 of last year crushed forecasts despite easing from Q3’s 4.9%. That could force Fed officials to refrain from easing policy, but the latest inflation data suggests they’re close to getting inflation to its 2% target.
- Nevertheless, mixed readings in other data suggest that risks have become more balanced. That is reflected by investors speculating that the Fed will cut rates by 139 basis points during 2024, according to the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) data.
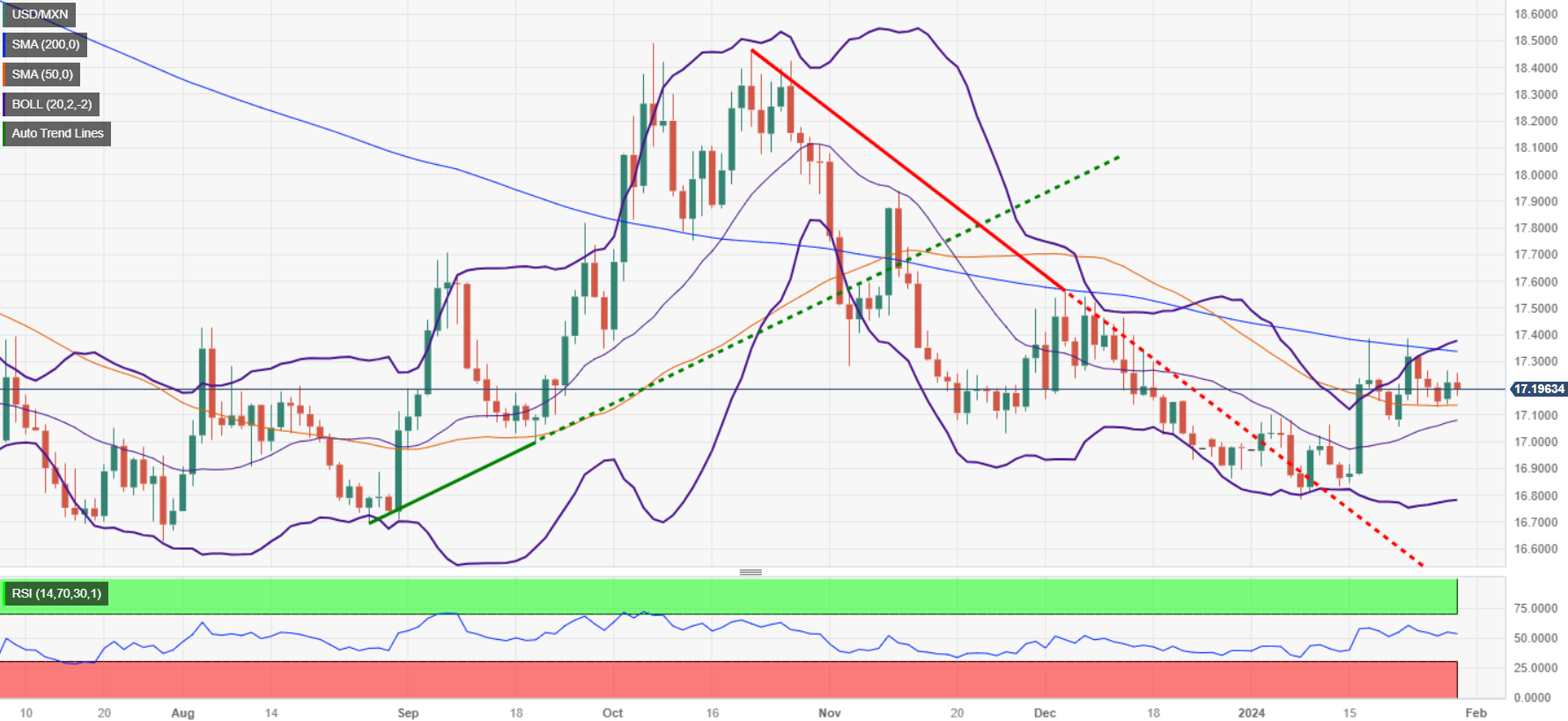
Technical Analysis: Mexican Peso status firm as USD/MXN hovers near 17.20
The USD/MXN trades sideways and is about to form an ascending triangle. The 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 17.34 is the first resistance level. If buyers conquer that level, the next stop would be the 100-day SMA at 17.41, followed by the December 9 high at 17.56. Last of all sits the May 23 high from last year at 17.99.
On the flipside, although a less likely scenario, the USD/MXN exchange rate could drop below the 50-day SMA at 17.13. A breach of the latter will expose the January 22 low at 17.05, followed by the 17.00 psychological level.
USD/MXN Price Action – Daily Chart
Banxico FAQs
The Bank of Mexico, also known as Banxico, is the country’s central bank. Its mission is to preserve the value of Mexico’s currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN), and to set the monetary policy. To this end, its main objective is to maintain low and stable inflation within target levels – at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%.
The main tool of the Banxico to guide monetary policy is by setting interest rates. When inflation is above target, the bank will attempt to tame it by raising rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money and thus cooling the economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN. The rate differential with the USD, or how the Banxico is expected to set interest rates compared with the US Federal Reserve (Fed), is a key factor.
Banxico meets eight times a year, and its monetary policy is greatly influenced by decisions of the US Federal Reserve (Fed). Therefore, the central bank’s decision-making committee usually gathers a week after the Fed. In doing so, Banxico reacts and sometimes anticipates monetary policy measures set by the Federal Reserve. For example, after the Covid-19 pandemic, before the Fed raised rates, Banxico did it first in an attempt to diminish the chances of a substantial depreciation of the Mexican Peso (MXN) and to prevent capital outflows that could destabilize the country.